Values With Uncertainty
Last updated on 2025-12-10
Overview
This article explains how ranges and Monte Carlo simulations as well as different distribution shapes are used in xP&A to model uncertainty in formulas, enabling more realistic and probabilistic forecasting.
This article contains the following sections:
Ranges and the Monte Carlo Method
When variables are in the format of a range (e.g. 0 to 100, uniform(0,100), a Monte Carlo simulation is run to estimate the possible outcomes of an uncertain event. Monte Carlo will randomly pick a value from the distribution and compute the whole model as if it were that random constant value. This process is repeated multiple times to generate distributions for the output variables.
The use of the simulation allows xP&A to perform computations using values with uncertainty that are not possible without it. Due to this method of handling uncertainty, you may notice that the range of the cell and the value are not the numbers you input or would expect, but only by a trivial amount.
Distribution Shapes
There are many different types of distribution shapes for values with uncertainty. Here are three examples of distributions that xP&A supports:
Triangular Distribution
Values in the format of '# to #' produce a triangle distribution where the center value is the most likely value, while the edges of the range are the least likely:
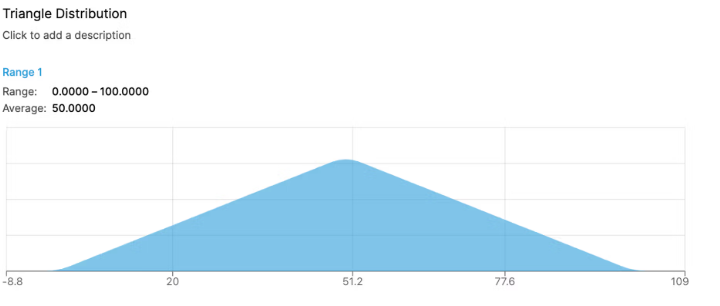 Chart with a Triangular Distribution
Chart with a Triangular Distribution
Uniform Distribution
Using the function of uniform(from, to), a uniform distribution can be produced:
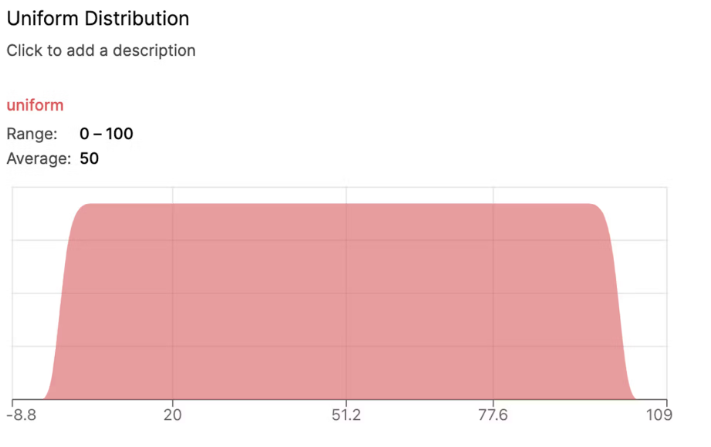 Chart with a Uniform Distribution
Chart with a Uniform Distribution
Poisson Distribution
Using the function poisson(lambda), a poisson distribution will be produced:
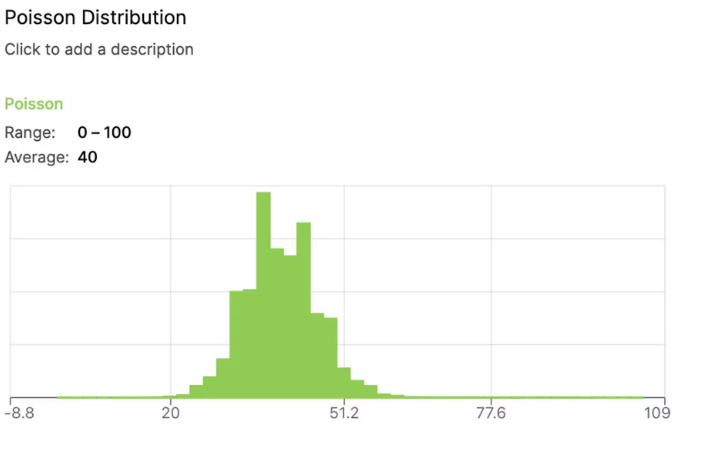 Chart with a Poisson Distribution
Chart with a Poisson Distribution
Sample
The sample function takes a random sample from the provided numbers. For example, sample(1,2,3) may return 1, 2 or 3 with equal probability.
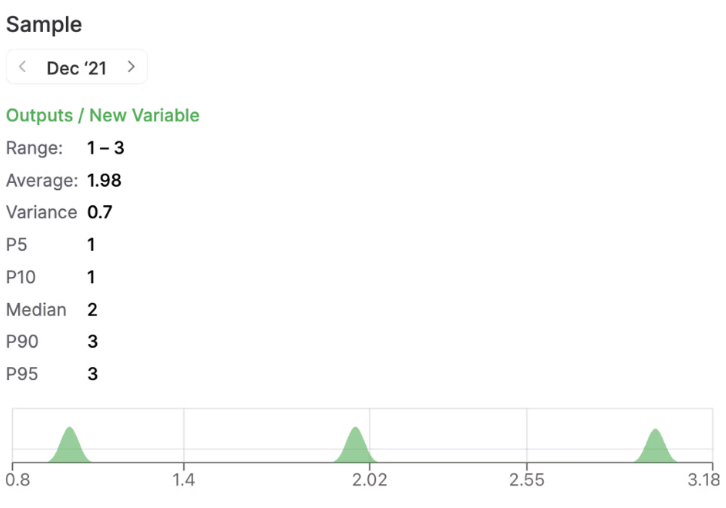 Chart with Sample function
Chart with Sample function